Chapter 6 Data Management
We will use the data set, Ames Housing Price data, from the AmesHousing package, containing 2930 observations and 81 features including the sale date and price. It’s a tibble but a dataframe version (Rbootcamp::ames) is also available in our package, Rbootcamp. And, we will introduce the dplyr package in many applications. See more about dplyr here.
library(AmesHousing)
library(dplyr)
amesdata <- make_ames()
glimpse(amesdata)## Rows: 2,930
## Columns: 81
## $ MS_SubClass <fct> One_Story_1946_and_Newer_All_Styles, One_Story_1946…
## $ MS_Zoning <fct> Residential_Low_Density, Residential_High_Density, …
## $ Lot_Frontage <dbl> 141, 80, 81, 93, 74, 78, 41, 43, 39, 60, 75, 0, 63,…
## $ Lot_Area <int> 31770, 11622, 14267, 11160, 13830, 9978, 4920, 5005…
## $ Street <fct> Pave, Pave, Pave, Pave, Pave, Pave, Pave, Pave, Pav…
## $ Alley <fct> No_Alley_Access, No_Alley_Access, No_Alley_Access, …
## $ Lot_Shape <fct> Slightly_Irregular, Regular, Slightly_Irregular, Re…
## $ Land_Contour <fct> Lvl, Lvl, Lvl, Lvl, Lvl, Lvl, Lvl, HLS, Lvl, Lvl, L…
## $ Utilities <fct> AllPub, AllPub, AllPub, AllPub, AllPub, AllPub, All…
## $ Lot_Config <fct> Corner, Inside, Corner, Corner, Inside, Inside, Ins…
## $ Land_Slope <fct> Gtl, Gtl, Gtl, Gtl, Gtl, Gtl, Gtl, Gtl, Gtl, Gtl, G…
## $ Neighborhood <fct> North_Ames, North_Ames, North_Ames, North_Ames, Gil…
## $ Condition_1 <fct> Norm, Feedr, Norm, Norm, Norm, Norm, Norm, Norm, No…
## $ Condition_2 <fct> Norm, Norm, Norm, Norm, Norm, Norm, Norm, Norm, Nor…
## $ Bldg_Type <fct> OneFam, OneFam, OneFam, OneFam, OneFam, OneFam, Twn…
## $ House_Style <fct> One_Story, One_Story, One_Story, One_Story, Two_Sto…
## $ Overall_Qual <fct> Above_Average, Average, Above_Average, Good, Averag…
## $ Overall_Cond <fct> Average, Above_Average, Above_Average, Average, Ave…
## $ Year_Built <int> 1960, 1961, 1958, 1968, 1997, 1998, 2001, 1992, 199…
## $ Year_Remod_Add <int> 1960, 1961, 1958, 1968, 1998, 1998, 2001, 1992, 199…
## $ Roof_Style <fct> Hip, Gable, Hip, Hip, Gable, Gable, Gable, Gable, G…
## $ Roof_Matl <fct> CompShg, CompShg, CompShg, CompShg, CompShg, CompSh…
## $ Exterior_1st <fct> BrkFace, VinylSd, Wd Sdng, BrkFace, VinylSd, VinylS…
## $ Exterior_2nd <fct> Plywood, VinylSd, Wd Sdng, BrkFace, VinylSd, VinylS…
## $ Mas_Vnr_Type <fct> Stone, None, BrkFace, None, None, BrkFace, None, No…
## $ Mas_Vnr_Area <dbl> 112, 0, 108, 0, 0, 20, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6…
## $ Exter_Qual <fct> Typical, Typical, Typical, Good, Typical, Typical, …
## $ Exter_Cond <fct> Typical, Typical, Typical, Typical, Typical, Typica…
## $ Foundation <fct> CBlock, CBlock, CBlock, CBlock, PConc, PConc, PConc…
## $ Bsmt_Qual <fct> Typical, Typical, Typical, Typical, Good, Typical, …
## $ Bsmt_Cond <fct> Good, Typical, Typical, Typical, Typical, Typical, …
## $ Bsmt_Exposure <fct> Gd, No, No, No, No, No, Mn, No, No, No, No, No, No,…
## $ BsmtFin_Type_1 <fct> BLQ, Rec, ALQ, ALQ, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ, ALQ, GLQ, Unf, U…
## $ BsmtFin_SF_1 <dbl> 2, 6, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3, 7, 7, 1, 7, 3, 3, 1, 3, …
## $ BsmtFin_Type_2 <fct> Unf, LwQ, Unf, Unf, Unf, Unf, Unf, Unf, Unf, Unf, U…
## $ BsmtFin_SF_2 <dbl> 0, 144, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1120, 0…
## $ Bsmt_Unf_SF <dbl> 441, 270, 406, 1045, 137, 324, 722, 1017, 415, 994,…
## $ Total_Bsmt_SF <dbl> 1080, 882, 1329, 2110, 928, 926, 1338, 1280, 1595, …
## $ Heating <fct> GasA, GasA, GasA, GasA, GasA, GasA, GasA, GasA, Gas…
## $ Heating_QC <fct> Fair, Typical, Typical, Excellent, Good, Excellent,…
## $ Central_Air <fct> Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, Y, …
## $ Electrical <fct> SBrkr, SBrkr, SBrkr, SBrkr, SBrkr, SBrkr, SBrkr, SB…
## $ First_Flr_SF <int> 1656, 896, 1329, 2110, 928, 926, 1338, 1280, 1616, …
## $ Second_Flr_SF <int> 0, 0, 0, 0, 701, 678, 0, 0, 0, 776, 892, 0, 676, 0,…
## $ Low_Qual_Fin_SF <int> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, …
## $ Gr_Liv_Area <int> 1656, 896, 1329, 2110, 1629, 1604, 1338, 1280, 1616…
## $ Bsmt_Full_Bath <dbl> 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, …
## $ Bsmt_Half_Bath <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, …
## $ Full_Bath <int> 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 3, 2, …
## $ Half_Bath <int> 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, …
## $ Bedroom_AbvGr <int> 3, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 1, 4, 4, …
## $ Kitchen_AbvGr <int> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, …
## $ Kitchen_Qual <fct> Typical, Typical, Good, Excellent, Typical, Good, G…
## $ TotRms_AbvGrd <int> 7, 5, 6, 8, 6, 7, 6, 5, 5, 7, 7, 6, 7, 5, 4, 12, 8,…
## $ Functional <fct> Typ, Typ, Typ, Typ, Typ, Typ, Typ, Typ, Typ, Typ, T…
## $ Fireplaces <int> 2, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, …
## $ Fireplace_Qu <fct> Good, No_Fireplace, No_Fireplace, Typical, Typical,…
## $ Garage_Type <fct> Attchd, Attchd, Attchd, Attchd, Attchd, Attchd, Att…
## $ Garage_Finish <fct> Fin, Unf, Unf, Fin, Fin, Fin, Fin, RFn, RFn, Fin, F…
## $ Garage_Cars <dbl> 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 2, …
## $ Garage_Area <dbl> 528, 730, 312, 522, 482, 470, 582, 506, 608, 442, 4…
## $ Garage_Qual <fct> Typical, Typical, Typical, Typical, Typical, Typica…
## $ Garage_Cond <fct> Typical, Typical, Typical, Typical, Typical, Typica…
## $ Paved_Drive <fct> Partial_Pavement, Paved, Paved, Paved, Paved, Paved…
## $ Wood_Deck_SF <int> 210, 140, 393, 0, 212, 360, 0, 0, 237, 140, 157, 48…
## $ Open_Porch_SF <int> 62, 0, 36, 0, 34, 36, 0, 82, 152, 60, 84, 21, 75, 0…
## $ Enclosed_Porch <int> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 170, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0…
## $ Three_season_porch <int> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, …
## $ Screen_Porch <int> 0, 120, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 144, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 140, …
## $ Pool_Area <int> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, …
## $ Pool_QC <fct> No_Pool, No_Pool, No_Pool, No_Pool, No_Pool, No_Poo…
## $ Fence <fct> No_Fence, Minimum_Privacy, No_Fence, No_Fence, Mini…
## $ Misc_Feature <fct> None, None, Gar2, None, None, None, None, None, Non…
## $ Misc_Val <int> 0, 0, 12500, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 500, 0, 0, 0, …
## $ Mo_Sold <int> 5, 6, 6, 4, 3, 6, 4, 1, 3, 6, 4, 3, 5, 2, 6, 6, 6, …
## $ Year_Sold <int> 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 201…
## $ Sale_Type <fct> WD , WD , WD , WD , WD , WD , WD , WD , WD , WD , W…
## $ Sale_Condition <fct> Normal, Normal, Normal, Normal, Normal, Normal, Nor…
## $ Sale_Price <int> 215000, 105000, 172000, 244000, 189900, 195500, 213…
## $ Longitude <dbl> -93.61975, -93.61976, -93.61939, -93.61732, -93.638…
## $ Latitude <dbl> 42.05403, 42.05301, 42.05266, 42.05125, 42.06090, 4…6.1 Filter
Suppose we want to find the houses that are sold in Jan 2010. You can use the function filter() in the dplyr package, a member of the tidyverse package. We can use subsetting operations.
amesdata[amesdata$Year_Sold == 2010 & amesdata$Mo_Sold == 1, ] ## # A tibble: 26 × 81
## MS_Sub…¹ MS_Zo…² Lot_F…³ Lot_A…⁴ Street Alley Lot_S…⁵ Land_…⁶ Utili…⁷ Lot_C…⁸
## <fct> <fct> <dbl> <int> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct>
## 1 One_Sto… Reside… 43 5005 Pave No_A… Slight… HLS AllPub Inside
## 2 One_Sto… Reside… 105 11751 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 3 Split_F… Reside… 85 10625 Pave No_A… Regular Lvl AllPub Inside
## 4 Two_Sto… Floati… 0 7500 Pave No_A… Regular Lvl AllPub Inside
## 5 Two_Sto… Reside… 102 12858 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 6 One_Sto… Reside… 100 18494 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Corner
## 7 One_Sto… Reside… 43 3203 Pave No_A… Regular Lvl AllPub Inside
## 8 Two_Sto… Reside… 60 17433 Pave No_A… Modera… Lvl AllPub CulDSac
## 9 Two_Sto… Reside… 76 10142 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 10 Two_Sto… Floati… 39 3515 Pave Paved Regular Lvl AllPub Inside
## # … with 16 more rows, 71 more variables: Land_Slope <fct>, Neighborhood <fct>,
## # Condition_1 <fct>, Condition_2 <fct>, Bldg_Type <fct>, House_Style <fct>,
## # Overall_Qual <fct>, Overall_Cond <fct>, Year_Built <int>,
## # Year_Remod_Add <int>, Roof_Style <fct>, Roof_Matl <fct>,
## # Exterior_1st <fct>, Exterior_2nd <fct>, Mas_Vnr_Type <fct>,
## # Mas_Vnr_Area <dbl>, Exter_Qual <fct>, Exter_Cond <fct>, Foundation <fct>,
## # Bsmt_Qual <fct>, Bsmt_Cond <fct>, Bsmt_Exposure <fct>, …Or we can use filter():
library(dplyr)
dplyr::filter(amesdata, Year_Sold == 2010, Mo_Sold == 1)## # A tibble: 26 × 81
## MS_Sub…¹ MS_Zo…² Lot_F…³ Lot_A…⁴ Street Alley Lot_S…⁵ Land_…⁶ Utili…⁷ Lot_C…⁸
## <fct> <fct> <dbl> <int> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct>
## 1 One_Sto… Reside… 43 5005 Pave No_A… Slight… HLS AllPub Inside
## 2 One_Sto… Reside… 105 11751 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 3 Split_F… Reside… 85 10625 Pave No_A… Regular Lvl AllPub Inside
## 4 Two_Sto… Floati… 0 7500 Pave No_A… Regular Lvl AllPub Inside
## 5 Two_Sto… Reside… 102 12858 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 6 One_Sto… Reside… 100 18494 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Corner
## 7 One_Sto… Reside… 43 3203 Pave No_A… Regular Lvl AllPub Inside
## 8 Two_Sto… Reside… 60 17433 Pave No_A… Modera… Lvl AllPub CulDSac
## 9 Two_Sto… Reside… 76 10142 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 10 Two_Sto… Floati… 39 3515 Pave Paved Regular Lvl AllPub Inside
## # … with 16 more rows, 71 more variables: Land_Slope <fct>, Neighborhood <fct>,
## # Condition_1 <fct>, Condition_2 <fct>, Bldg_Type <fct>, House_Style <fct>,
## # Overall_Qual <fct>, Overall_Cond <fct>, Year_Built <int>,
## # Year_Remod_Add <int>, Roof_Style <fct>, Roof_Matl <fct>,
## # Exterior_1st <fct>, Exterior_2nd <fct>, Mas_Vnr_Type <fct>,
## # Mas_Vnr_Area <dbl>, Exter_Qual <fct>, Exter_Cond <fct>, Foundation <fct>,
## # Bsmt_Qual <fct>, Bsmt_Cond <fct>, Bsmt_Exposure <fct>, …6.2 Arrange
Let’s find the 10 houses with the highest sale prices by year.
ar <- arrange(amesdata, Year_Sold, desc(Sale_Price))
ar## # A tibble: 2,930 × 81
## MS_Sub…¹ MS_Zo…² Lot_F…³ Lot_A…⁴ Street Alley Lot_S…⁵ Land_…⁶ Utili…⁷ Lot_C…⁸
## <fct> <fct> <dbl> <int> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct>
## 1 Two_Sto… Reside… 118 35760 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub CulDSac
## 2 Two_Sto… Reside… 114 17242 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 3 Two_Sto… Reside… 85 16056 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 4 Two_Sto… Reside… 60 18062 Pave No_A… Slight… HLS AllPub CulDSac
## 5 Two_Sto… Reside… 82 16052 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub CulDSac
## 6 Two_and… Reside… 90 22950 Pave No_A… Modera… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 7 One_Sto… Reside… 90 18261 Pave No_A… Slight… HLS AllPub Inside
## 8 One_Sto… Reside… 107 13891 Pave No_A… Regular Lvl AllPub Inside
## 9 Two_Sto… Reside… 59 16023 Pave No_A… Slight… HLS AllPub CulDSac
## 10 Two_Sto… Reside… 66 13682 Pave No_A… Modera… HLS AllPub CulDSac
## # … with 2,920 more rows, 71 more variables: Land_Slope <fct>,
## # Neighborhood <fct>, Condition_1 <fct>, Condition_2 <fct>, Bldg_Type <fct>,
## # House_Style <fct>, Overall_Qual <fct>, Overall_Cond <fct>,
## # Year_Built <int>, Year_Remod_Add <int>, Roof_Style <fct>, Roof_Matl <fct>,
## # Exterior_1st <fct>, Exterior_2nd <fct>, Mas_Vnr_Type <fct>,
## # Mas_Vnr_Area <dbl>, Exter_Qual <fct>, Exter_Cond <fct>, Foundation <fct>,
## # Bsmt_Qual <fct>, Bsmt_Cond <fct>, Bsmt_Exposure <fct>, …Or
arr <- amesdata[order(amesdata$Year_Sold, desc(amesdata$Sale_Price)), ]
head(arr)## # A tibble: 6 × 81
## MS_SubC…¹ MS_Zo…² Lot_F…³ Lot_A…⁴ Street Alley Lot_S…⁵ Land_…⁶ Utili…⁷ Lot_C…⁸
## <fct> <fct> <dbl> <int> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct> <fct>
## 1 Two_Stor… Reside… 118 35760 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub CulDSac
## 2 Two_Stor… Reside… 114 17242 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 3 Two_Stor… Reside… 85 16056 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub Inside
## 4 Two_Stor… Reside… 60 18062 Pave No_A… Slight… HLS AllPub CulDSac
## 5 Two_Stor… Reside… 82 16052 Pave No_A… Slight… Lvl AllPub CulDSac
## 6 Two_and_… Reside… 90 22950 Pave No_A… Modera… Lvl AllPub Inside
## # … with 71 more variables: Land_Slope <fct>, Neighborhood <fct>,
## # Condition_1 <fct>, Condition_2 <fct>, Bldg_Type <fct>, House_Style <fct>,
## # Overall_Qual <fct>, Overall_Cond <fct>, Year_Built <int>,
## # Year_Remod_Add <int>, Roof_Style <fct>, Roof_Matl <fct>,
## # Exterior_1st <fct>, Exterior_2nd <fct>, Mas_Vnr_Type <fct>,
## # Mas_Vnr_Area <dbl>, Exter_Qual <fct>, Exter_Cond <fct>, Foundation <fct>,
## # Bsmt_Qual <fct>, Bsmt_Cond <fct>, Bsmt_Exposure <fct>, …6.3 Pipe
Pipes help us apply multiple operations sequentially on a given data.
library(ggplot2)
amesdata %>%
filter(Year_Sold == 2009, Mo_Sold == 1) %>%
arrange(Year_Built) %>%
ggplot(mapping = aes(x = Lot_Area, y = Sale_Price)) +
geom_point()
6.4 Select
How do we select variables based on some characteristics
amesdata %>% select(starts_with("Year"), Sale_Price)## # A tibble: 2,930 × 4
## Year_Built Year_Remod_Add Year_Sold Sale_Price
## <int> <int> <int> <int>
## 1 1960 1960 2010 215000
## 2 1961 1961 2010 105000
## 3 1958 1958 2010 172000
## 4 1968 1968 2010 244000
## 5 1997 1998 2010 189900
## 6 1998 1998 2010 195500
## 7 2001 2001 2010 213500
## 8 1992 1992 2010 191500
## 9 1995 1996 2010 236500
## 10 1999 1999 2010 189000
## # … with 2,920 more rowsamesdata %>% select(contains("Mo"))## # A tibble: 2,930 × 2
## Year_Remod_Add Mo_Sold
## <int> <int>
## 1 1960 5
## 2 1961 6
## 3 1958 6
## 4 1968 4
## 5 1998 3
## 6 1998 6
## 7 2001 4
## 8 1992 1
## 9 1996 3
## 10 1999 6
## # … with 2,920 more rows6.5 Create & group_by()
We may want to create new variables as functions of the existing ones by mutate():
library(r02pro)
library(tidyverse)
amesdata %>%
select(Overall_Qual, Lot_Area, Sale_Price) %>%
mutate(ave_price = Sale_Price/Lot_Area) ## # A tibble: 2,930 × 4
## Overall_Qual Lot_Area Sale_Price ave_price
## <fct> <int> <int> <dbl>
## 1 Above_Average 31770 215000 6.77
## 2 Average 11622 105000 9.03
## 3 Above_Average 14267 172000 12.1
## 4 Good 11160 244000 21.9
## 5 Average 13830 189900 13.7
## 6 Above_Average 9978 195500 19.6
## 7 Very_Good 4920 213500 43.4
## 8 Very_Good 5005 191500 38.3
## 9 Very_Good 5389 236500 43.9
## 10 Good 7500 189000 25.2
## # … with 2,920 more rowsCan we summarize by groups? First let’s see an example for summarize:
amesdata %>%
summarize(n_houses = n(),
ave_liv_area = mean(Lot_Area),
prob = c(0.25, 0.75),
q_price = quantile(Sale_Price, c(0.25, 0.75),
na.rm = TRUE))## # A tibble: 2 × 4
## n_houses ave_liv_area prob q_price
## <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2930 10148. 0.25 129500
## 2 2930 10148. 0.75 213500Another
amesdata %>%
group_by(Overall_Qual) %>%
summarize(n_houses = n(),
ave_liv_area = mean(Lot_Area),
ave_price = mean(Sale_Price),
na.rm = TRUE)## # A tibble: 10 × 5
## Overall_Qual n_houses ave_liv_area ave_price na.rm
## <fct> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <lgl>
## 1 Very_Poor 4 15214. 48725 TRUE
## 2 Poor 13 9326. 52325. TRUE
## 3 Fair 40 9439. 83186. TRUE
## 4 Below_Average 226 8464. 106485. TRUE
## 5 Average 825 9996. 134753. TRUE
## 6 Above_Average 732 9788. 162130. TRUE
## 7 Good 602 10309. 205026. TRUE
## 8 Very_Good 350 10618. 270914. TRUE
## 9 Excellent 107 12777. 368337. TRUE
## 10 Very_Excellent 31 18071. 450217. TRUE6.6 More tools
6.6.1 subset()
any(is.na(amesdata))## [1] FALSE#Pay attention to subset(). This will be a time-saver
sub <- subset(amesdata, amesdata$Overall_Qual != "Fair")
dim(sub)## [1] 2890 81dim(amesdata)## [1] 2930 81#You can drop columns (variables) as well
amesless = subset(amesdata, select = c("Sale_Type", "Mo_Sold"))
head(amesless)## # A tibble: 6 × 2
## Sale_Type Mo_Sold
## <fct> <int>
## 1 "WD " 5
## 2 "WD " 6
## 3 "WD " 6
## 4 "WD " 4
## 5 "WD " 3
## 6 "WD " 6However, look at the help(subset): “This is a convenience function intended for use interactively. For programming it is better to use the standard subsetting functions like [ ], and in particular the non-standard evaluation of argument subset can have unanticipated consequences”.
6.6.2 within() & with()
Here is an example to use within():
ana <- within(amesdata, Sale_Price[Fence != 2] <- 0)
#which is a short cut of
amesdata$Sale_Price[amesdata$Fence != 2] <- 0And with()
mean(with(amesdata, Sale_Price[Mo_Sold == 5 & Overall_Qual =="Good"]))## [1] 06.6.3 aggregate()
The aggregate() function in R can be used to calculate summary statistics for a dataset.
#create data frame
df <- data.frame(team=c('A', 'A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'B'),
position=c('G', 'G', 'F', 'G', 'F', 'F'),
points=c(99, 90, 86, 88, 95, 99),
assists=c(33, 28, 31, 39, 34, 23),
rebounds=c(30, 28, 24, 24, 28, 33))
df## team position points assists rebounds
## 1 A G 99 33 30
## 2 A G 90 28 28
## 3 A F 86 31 24
## 4 B G 88 39 24
## 5 B F 95 34 28
## 6 B F 99 23 33#find mean points by team
aggregate(df$points, by=list(df$team), FUN=mean)## Group.1 x
## 1 A 91.66667
## 2 B 94.00000aggregate(df$points, by=list(df$team, df$position), FUN=mean)## Group.1 Group.2 x
## 1 A F 86.0
## 2 B F 97.0
## 3 A G 94.5
## 4 B G 88.0We can also define our own functions
mine <- function(x){
return(sort(x))
}
aggregate(df$points, by=list(df$assists), FUN=mine)## Group.1 x
## 1 23 99
## 2 28 90
## 3 31 86
## 4 33 99
## 5 34 95
## 6 39 886.7 Tables
Here, we’ll look at two-way tables.
6.7.1 From Data with table()
Most data tables use categorical variables. Here is definition of input from table():
One or more objects which can be interpreted as factors (including numbers or character strings), or a list (such as a data frame) whose components can be so interpreted.
tb1 <- table(amesdata$Lot_Shape, amesdata$House_Style)
tb1##
## One_and_Half_Fin One_and_Half_Unf One_Story SFoyer SLvl
## Regular 266 18 926 54 65
## Slightly_Irregular 44 1 514 29 61
## Moderately_Irregular 3 0 35 0 2
## Irregular 1 0 6 0 0
##
## Two_and_Half_Fin Two_and_Half_Unf Two_Story
## Regular 6 17 507
## Slightly_Irregular 1 6 323
## Moderately_Irregular 1 0 35
## Irregular 0 1 8tb2 <- table(amesdata$Lot_Shape, amesdata$House_Style, amesdata$Street)
tb2## , , = Grvl
##
##
## One_and_Half_Fin One_and_Half_Unf One_Story SFoyer SLvl
## Regular 1 0 6 1 0
## Slightly_Irregular 1 0 1 0 0
## Moderately_Irregular 0 0 1 0 0
## Irregular 0 0 0 0 0
##
## Two_and_Half_Fin Two_and_Half_Unf Two_Story
## Regular 0 0 1
## Slightly_Irregular 0 0 0
## Moderately_Irregular 0 0 0
## Irregular 0 0 0
##
## , , = Pave
##
##
## One_and_Half_Fin One_and_Half_Unf One_Story SFoyer SLvl
## Regular 265 18 920 53 65
## Slightly_Irregular 43 1 513 29 61
## Moderately_Irregular 3 0 34 0 2
## Irregular 1 0 6 0 0
##
## Two_and_Half_Fin Two_and_Half_Unf Two_Story
## Regular 6 17 506
## Slightly_Irregular 1 6 323
## Moderately_Irregular 1 0 35
## Irregular 0 1 8See what happens if you a continuous variable amesdata$Lot_Area:
#tb2 <- table(amesdata$Lot_Shape, amesdata$Lot_Area, amesdata$Street)
#tb26.7.2 datatable()
If we have more columns:
DT::datatable(amesdata, rownames = FALSE, filter="top", options = list(pageLength = 10, scrollX=T) )6.7.3 With describr
The package describr has several good functions
library(descriptr)
ds_screener(mtcars)## ----------------------------------------------------------------------
## | Column Name | Data Type | Levels | Missing | Missing (%) |
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------
## | mpg | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## | cyl | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## | disp | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## | hp | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## | drat | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## | wt | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## | qsec | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## | vs | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## | am | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## | gear | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## | carb | numeric | NA | 0 | 0 |
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------
##
## Overall Missing Values 0
## Percentage of Missing Values 0 %
## Rows with Missing Values 0
## Columns With Missing Values 0One continuous one factor:
mtcars$cyl <- as.factor(mtcars$cyl)
ds_group_summary(mtcars, cyl, mpg)## mpg by cyl
## -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## | Statistic/Levels| 4| 6| 8|
## -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## | Obs| 11| 7| 14|
## | Minimum| 21.4| 17.8| 10.4|
## | Maximum| 33.9| 21.4| 19.2|
## | Mean| 26.66| 19.74| 15.1|
## | Median| 26| 19.7| 15.2|
## | Mode| 22.8| 21| 10.4|
## | Std. Deviation| 4.51| 1.45| 2.56|
## | Variance| 20.34| 2.11| 6.55|
## | Skewness| 0.35| -0.26| -0.46|
## | Kurtosis| -1.43| -1.83| 0.33|
## | Uncorrected SS| 8023.83| 2741.14| 3277.34|
## | Corrected SS| 203.39| 12.68| 85.2|
## | Coeff Variation| 16.91| 7.36| 16.95|
## | Std. Error Mean| 1.36| 0.55| 0.68|
## | Range| 12.5| 3.6| 8.8|
## | Interquartile Range| 7.6| 2.35| 1.85|
## -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------6.7.4 xtabs() & ftabs()
The xtabs() & ftabs() functions allows you to quickly calculate frequencies for more factor variables.
library(RBootcamp)
nt <- ftable(xtabs(~ year + maturity.stage + month, data = squid1))
nt## month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
## year maturity.stage
## 1989 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2
## 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3
## 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5
## 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2
## 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
## 1990 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 8 0 1 1 1 2
## 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 22 21 76 17 31 4
## 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 5 1 31 6
## 4 2 0 15 7 0 0 4 3 0 0 10 13
## 5 1 0 25 3 1 0 8 0 0 0 3 6
## 1991 1 0 0 0 2 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 0
## 2 1 1 0 1 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 0
## 3 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
## 4 16 8 6 13 6 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
## 5 18 21 23 16 23 3 0 0 0 0 0 06.7.5 Table with manual entry
smoke <- matrix(c(51,43,22,92,28,21,68,22,9),ncol=3,byrow=TRUE)
colnames(smoke) <- c("High","Low","Middle")
rownames(smoke) <- c("current","former","never")
smoke <- as.table(smoke)
smoke## High Low Middle
## current 51 43 22
## former 92 28 21
## never 68 22 96.7.6 Tools for tables
margin.table(smoke, 1)## current former never
## 116 141 99margin.table(smoke, 2)## High Low Middle
## 211 93 52smoke/margin.table(smoke)## High Low Middle
## current 0.14325843 0.12078652 0.06179775
## former 0.25842697 0.07865169 0.05898876
## never 0.19101124 0.06179775 0.02528090prop.table(smoke)## High Low Middle
## current 0.14325843 0.12078652 0.06179775
## former 0.25842697 0.07865169 0.05898876
## never 0.19101124 0.06179775 0.02528090mosaicplot(smoke,main="Smokers",xlab="Status",ylab="Economic Class")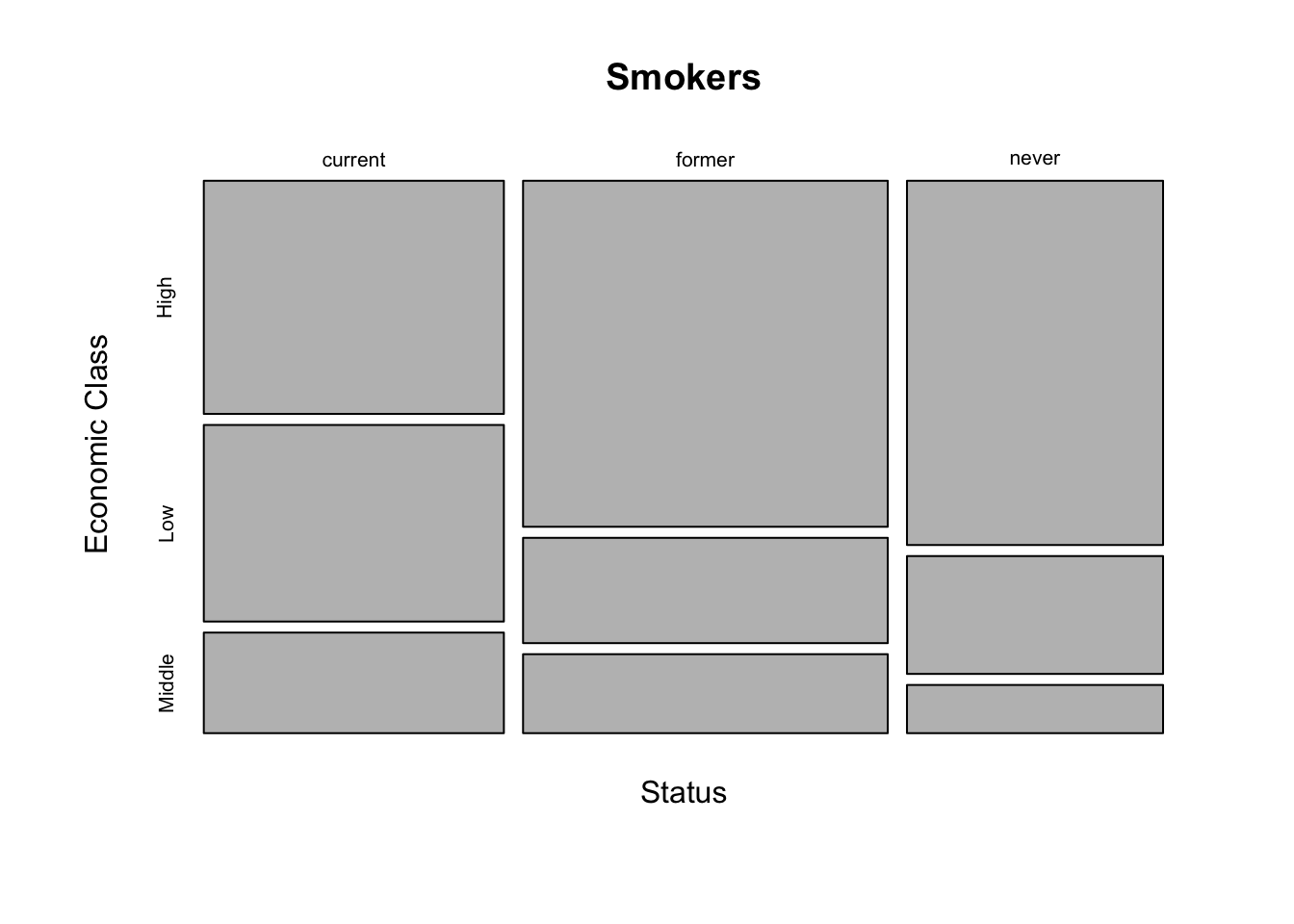
6.8 merge()
The merge() function merges two data frames by common columns or row names, or do other versions of database join operations. Here is an example:
df1 = data.frame(StudentId = c(1:6),
Marks = c("70", "84", "90", "93", "80", "76"))
df2 = data.frame(StudentId = c(2, 4, 6, 7, 8),
city = c("Lahore", "Karachi", "Peshawar", "Quetta", "Multan"))
df3 = merge(df1, df2, by = "StudentId")
df3## StudentId Marks city
## 1 2 84 Lahore
## 2 4 93 Karachi
## 3 6 76 Peshawardf4 = merge(df1, df2, by = "StudentId", all = TRUE)
df4## StudentId Marks city
## 1 1 70 <NA>
## 2 2 84 Lahore
## 3 3 90 <NA>
## 4 4 93 Karachi
## 5 5 80 <NA>
## 6 6 76 Peshawar
## 7 7 <NA> Quetta
## 8 8 <NA> MultanSee the options of merge() by ?merge. We can do the same operation in dplyr:
library(dplyr)
df3= df1 %>% inner_join(df2,by="StudentId")
df3## StudentId Marks city
## 1 2 84 Lahore
## 2 4 93 Karachi
## 3 6 76 Peshawar